Introduction To Microwave Chemical Reactor
Microwave chemical reactor is a special device for chemical reaction using microwave radiation. The reactor consists of a microwave source generating electromagnetic radiation, a reaction vessel containing a reaction mixture and a temperature control system. Microwave radiation is used because it efficiently and rapidly heats the reaction mixture, thereby speeding up the reaction and increasing the yield. The high energy of the microwaves causes polar and ionic molecules in the reaction mixture to vibrate, generating heat. This process is known as dielectric heating.

Hot Models:
WBFY-201 microwave chemical reactor
Rated output power: 1100W
Microwave frequency: 2450+50MHz
Internal material: polyester paint sprayed steel plate
WBFY-205 microwave chemical reactor
Rated output power: 1100W
Microwave frequency: 2450+50MHz microwave adjustable
Internal material: stainless steel plate
MCR-3 microwave chemical reactor
Microwave output power: ≤750W (continuous automatic adjustment)
Weibo output mode: continuous wave
Microwave frequency: 2450+15MHz
Maximum operating temperature: ≤250°C (optional setting)

Applicable Industries Of Microwave Chemical Reactor:
Pharmaceutical industry:
Laboratory microwave reactors can be used to synthesize various pharmaceutical compounds, including active pharmaceutical ingredients (API) and intermediates.
Chemical industry:
The laboratory microwave reactor can be used to synthesize various chemicals such as polymers, nanoparticles and catalysts.
Material science:
Laboratory microwave reactors can be used to synthesize various materials such as ceramics, metal alloys and composites.
Food processing:
Laboratory microwave reactor can be used in various food processing, such as sterilization, dehydration, cooking, etc.
Environmental Science:
Laboratory microwave reactor can be used for wastewater treatment, soil remediation and air pollution control.
Energy industry:
Laboratory microwave reactors can be used to synthesize various energy-related materials, such as battery electrodes, fuel cells, etc.
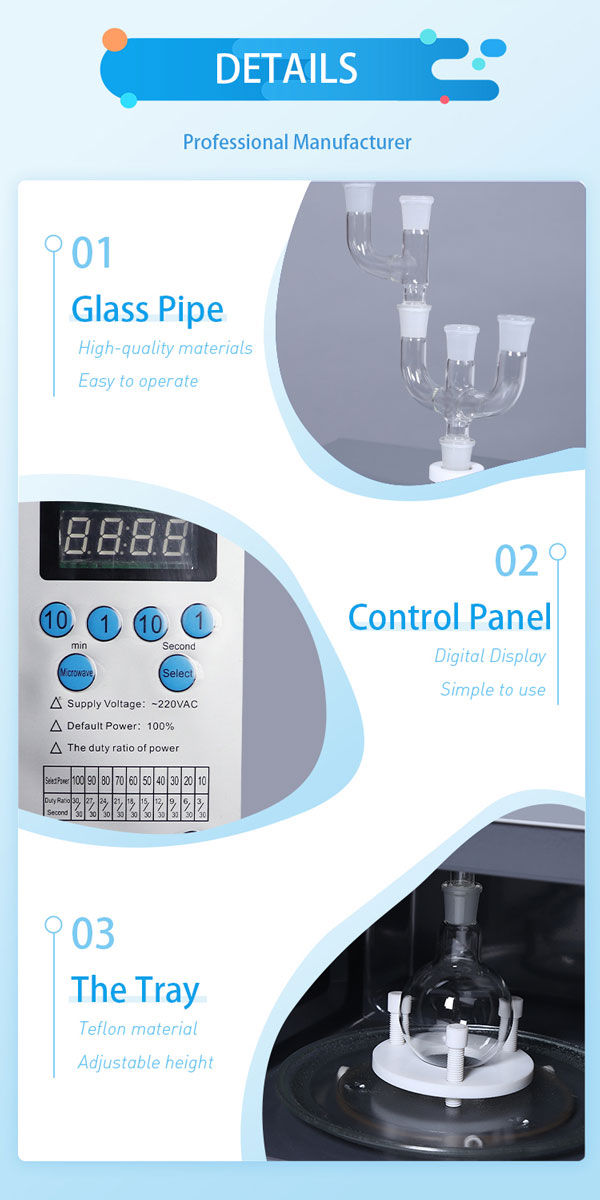
Operation Of Microwave Chemical Reactor
Microwave chemical reactors are used for fast and efficient chemical synthesis or processing using microwave radiation. The general operation of a microwave chemical reactor includes the following steps:
Load the reactor:
Add the reactants to the reaction vessel of the microwave chemical reactor.
Seal the reactor:
Reaction vessels are sealed with suitable lids or lids to prevent escape of reactants or products.
Adjustment parameters:
Adjust reaction conditions such as temperature, pressure, and power to desired values using the control panel of the microwave chemical reactor.
Start the microwave:
Turn on the microwave generator and expose the reaction vessel to microwave radiation.
Monitor response:
The progress of the reaction was monitored by periodically sampling the reaction mixture.
To stop microwave:
Once the required reaction time has elapsed, the microwave generator is switched off.
Cool the reaction mixture:
The reaction mixture was allowed to cool, and the product was collected.
Parameter
| Model | WBFY-201 | WBFY-205 |
| Rated power consumption(W) | 1100 | 1100 |
| Rated maximum output power(W) | 750 | 650 |
| Maximum input current(A) | 7.8 | 7.8 |
| Operating voltage(V) | 220 | 220 |
| Frequency(Mhz) | 2450±50 | 2450±50 |
| Chamber size(mm) | 290*295*190 | 290*295*190 |
| Overall size (mm) | 480*340*280 | 480*340*380 |
| G.W. (Kg) | 20 | 35 |
FAQ
Q: What types of reactions can be performed in a microwave chemical reactor?
A: Various chemical reactions can be carried out in the laboratory microwave reactor, including organic reactions, inorganic reactions and polymerization reactions. Some common examples include the synthesis of nanoparticles, the formation of organometallic compounds, and the production of pharmaceuticals.
Q: How does microwave chemical reactor work?
A: A laboratory microwave reactor works by heating a reaction mixture using microwave radiation. Microwaves cause polar molecules in the sample to rotate, which generates heat through friction. This allows the sample to be heated quickly and evenly.
Q: What are the limitations of microwave chemical reactor?
A: The limitations of the laboratory microwave reactor include possible thermal gradients, the need for specialized reaction vessels, and possible interference from microwave radiation. It is important to optimize reaction conditions to minimize these limitations.

